library(gwid)
#>
#> Attaching package: 'gwid'
#> The following objects are masked from 'package:base':
#>
#> print, subsetgwid is an R-package designed for the analysis of IBD (Identity by Descent) data, to discover rare alleles (susceptibility regions) associated with case-control phenotype. Although Genome Wide Association Studies (GWAS) successfully reveal numerous common variants linked to diseases, they exhibit lack of power to identify rare alleles. To address this limitation, we have developed a pipeline that employs IBD data (output of refined-IBD software). This methodology encompasses a sequential process for analyzing the aforementioned data within isolated populations. The primary objective of this approach is to enhance the sensitivity of variant detection by utilizing information from genetically related individuals, thereby facilitating the identification of causal variants. An overall representation of the pipeline is visually depicted in the following figure.

gwid pipeline
Usage
The gwid package receives four types of inputs: a
genotype file, an IBD file, a haplotype file, and phenotype file. The
genotype data is derived from the output of the SNPRelate
package in the form of a gds file. The IBD file takes
the form of tabulated data produced by the Refined
IBD software. Haplotype file comes from the output of the Beagle,
while phenotype data is represented using an R list.
Installation
You can install the stable version of gwid from CRAN with:
if (!require("BiocManager", quietly = TRUE))
install.packages("BiocManager")
BiocManager::install(c("SNPRelate","gdsfmt"))
install.packages("gwid")Alternatively, you can install the stable version of
gwid with:
if (!require("BiocManager", quietly = TRUE))
install.packages("BiocManager")
BiocManager::install("gwid")You can install the development version of gwid from GitHub with:
# install.packages("devtools")
devtools::install_github("soroushmdg/gwid")Example
We demonstrated the key functionalities of gwid using the rheumatoid
arthritis (RA) GWAS dataset. This dataset consisted of DNA samples
collected from 478 individuals diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
and a control group of 1,434 individuals without RA. Genotyping was
performed using the Illumina Infinium array. All samples were obtained
from a genetically homogeneous population in central Wisconsin
exhibiting elevated relatedness structure. Because size of data is
large, we use pggyback package to upload and download data
from github repository.
# install.packages("piggyback")
piggyback::pb_download(repo = "soroushmdg/gwid",
tag = "v0.0.1",
dest = tempdir())
ibd_data_file <- paste0(tempdir(), "//chr3.ibd")
genome_data_file <- paste0(tempdir(), "//chr3.gds")
phase_data_file <- paste0(tempdir(), "//chr3.vcf")
case_control_data_file <- paste0(tempdir(), "//case-cont-RA.withmap.Rda")Input
In this code we explain each input data files individually.
case_control is object of class caco that has
phenotype information. snp_data_gds object of class
gwas read output of SNPRelate package, we use
this package because it is very fast and efficient.
haplotype_data object of class phase has
haplotype data. ibd_data is an object of gwid
class that has IBD information.
library(gwid)
# case-control data
case_control <- gwid::case_control(case_control_rda = case_control_data_file)
names(case_control) #cases and controls group
#> [1] "cases" "case1" "case2" "cont1" "cont2" "cont3"
summary(case_control) # in here, we only consider cases,cont1,cont2,cont3
#> Length Class Mode
#> cases 478 -none- character
#> case1 178 -none- character
#> case2 300 -none- character
#> cont1 477 -none- character
#> cont2 478 -none- character
#> cont3 478 -none- character
#groups in the study
case_control$cases[1:3] # first three subject names of cases group
#> [1] "MC.154405@1075678440" "MC.154595@1075642175" "MC.154701@1076254706"
# read SNP data (use SNPRelate to convert it to gds) and count number of
#minor alleles
snp_data_gds <- gwid::build_gwas(gds_data = genome_data_file,
caco = case_control,
gwas_generator = TRUE)
class(snp_data_gds)
#> [1] "gwas"
names(snp_data_gds)
#> [1] "smp.id" "snp.id" "snp.pos" "smp.indx" "smp.snp" "caco" "snps"
head(snp_data_gds$snps) # it has information about counts of minor alleles
#> Key: <snp_pos>
#> snp_pos case_control value
#> <int> <fctr> <int>
#> 1: 66894 cases 627
#> 2: 66894 case1 240
#> 3: 66894 case2 387
#> 4: 66894 cont1 639
#> 5: 66894 cont2 647
#> 6: 66894 cont3 646
#in each location.
# read haplotype data (output of beagle)
haplotype_data <- gwid::build_phase(phased_vcf = phase_data_file,
caco = case_control)
class(haplotype_data)
#> [1] "phase"
names(haplotype_data)
#> [1] "Hap.1" "Hap.2"
dim(haplotype_data$Hap.1) #22302 SNP and 1911 subjects
#> [1] 22302 1911
# read IBD data (output of Refined-IBD)
ibd_data <- gwid::build_gwid(ibd_data = ibd_data_file,
gwas = snp_data_gds)
class(ibd_data)
#> [1] "gwid"
ibd_data$ibd # refined IBD output
#> V1 V2 V3 V4 V5
#> <char> <int> <char> <int> <int>
#> 1: MC.AMD127769@0123889787 2 MC.160821@1075679055 1 3
#> 2: MC.AMD127769@0123889787 1 MC.AMD107154@0123908746 1 3
#> 3: MC.AMD127769@0123889787 2 9474283-1-0238040187 1 3
#> 4: MC.AMD127769@0123889787 1 MC.159487@1075679208 2 3
#> 5: MC.163045@1082086165 2 MC.160470@1075679095 1 3
#> ---
#> 377560: 1492602-1-0238095971 2 2235472-1-0238095471 2 3
#> 377561: 4618455-1-0238095900 2 3848034-1-0238094219 1 3
#> 377562: MC.160332@1075641581 2 9630188-1-0238038787 2 3
#> 377563: MC.AMD122238@0124011436 2 MC.159900@1076254946 1 3
#> 377564: MC.AMD105910@0123907456 1 7542312-1-0238039298 1 3
#> V6 V7 V8 V9
#> <int> <int> <num> <num>
#> 1: 32933295 34817627 3.26 1.884
#> 2: 29995340 31752607 4.35 1.757
#> 3: 34165785 35898774 6.36 1.733
#> 4: 21526766 23162240 8.71 1.635
#> 5: 11822616 13523010 5.29 1.700
#> ---
#> 377560: 194785443 196328849 4.92 1.543
#> 377561: 190235788 192423862 7.77 2.188
#> 377562: 184005719 186184328 5.95 2.179
#> 377563: 181482803 184801115 3.58 3.318
#> 377564: 182440135 183972729 3.03 1.533
ibd_data$res # count number of IBD for each SNP location
#> snp_pos case_control value
#> <num> <fctr> <num>
#> 1: 66894 cases 27
#> 2: 82010 cases 28
#> 3: 89511 cases 29
#> 4: 104972 cases 29
#> 5: 107776 cases 29
#> ---
#> 133808: 197687252 cont3 44
#> 133809: 197701913 cont3 44
#> 133810: 197744198 cont3 44
#> 133811: 197762623 cont3 44
#> 133812: 197833758 cont3 44
plot method
The plot function can be applied to the
gwid class to display the counts of IBD in each Single SNP
among both case and control groups. By utilizing the
ly=TRUE parameter, the user has the option to transform the
plot into a plotly object, facilitating interactive
exploration of the entire chromosome or specific regions of interest
through the use of snp_start and snp_end
parameters. Additionally, the y parameter enables the
inclusion of only specific groups of subjects for consideration.
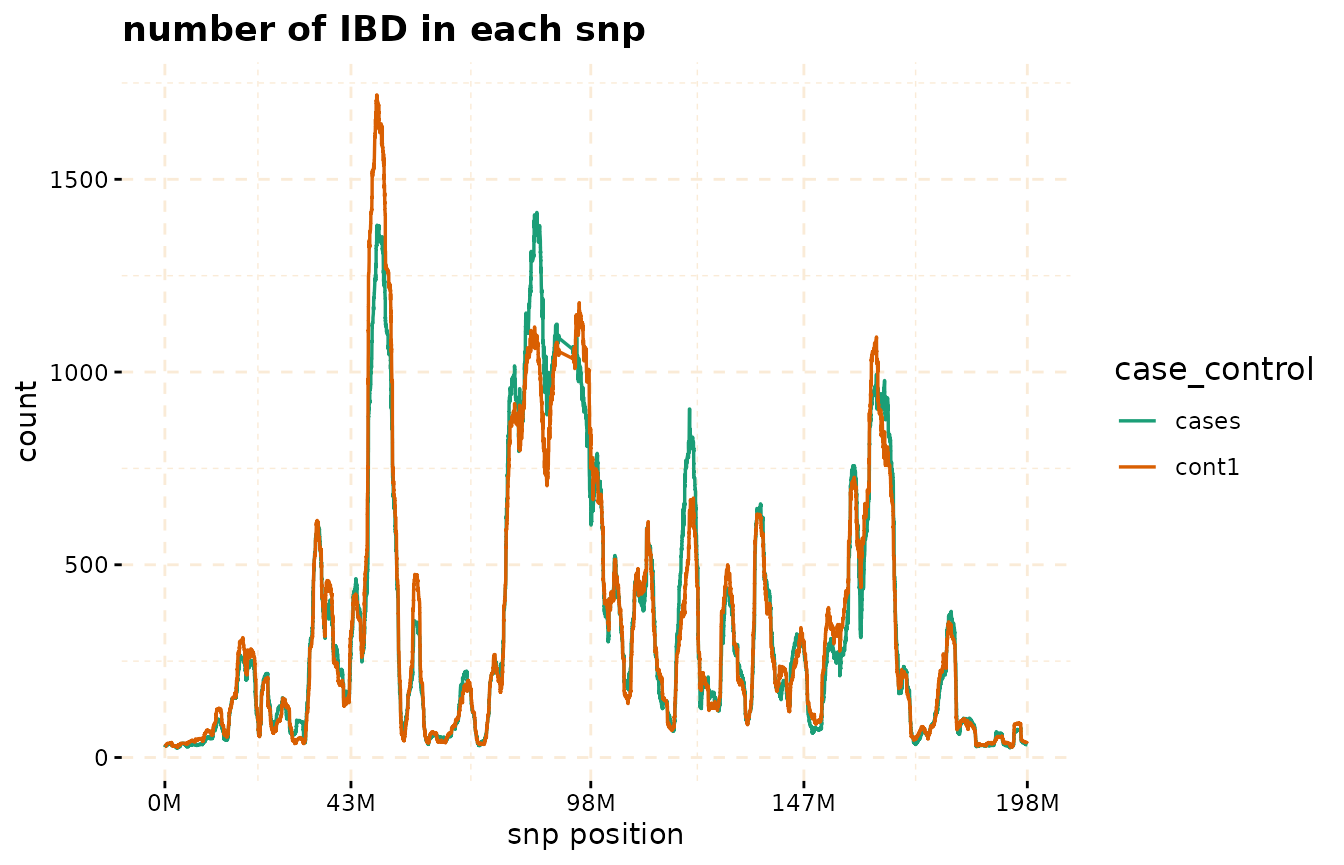
# Further investigate location between 117M and 122M
# significant number of IBD's in group cases, compare to cont1, cont2 and cont3.
plot(ibd_data,
y = c("cases","cont1"),
snp_start = 117026294,
snp_end = 122613594,
ly=FALSE) 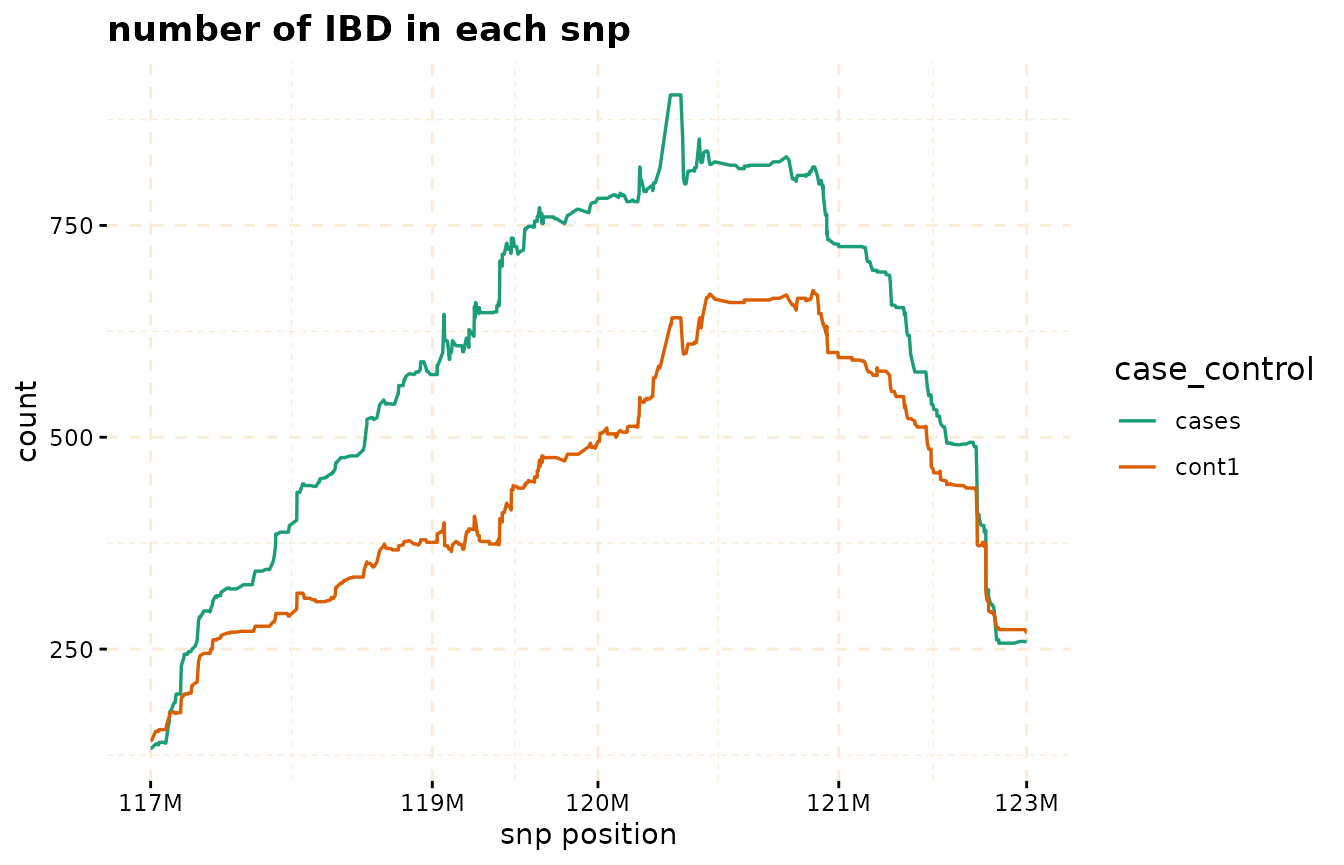
Through the utilization of the fisher_test method, it
becomes possible to calculate p-values within chosen regions. These
p-values help assess whether there are noteworthy differences in counts
between the case and control groups.
model_fisher <- gwid::fisher_test(ibd_data,
case_control,
reference = "cases",
snp_start = 117026294,
snp_end = 122613594)
class(model_fisher)
#> [1] "test_snps" "data.table" "data.frame"
plot(model_fisher,
y = c("cont1","cont2"),
ly=FALSE,
log_transformation = TRUE)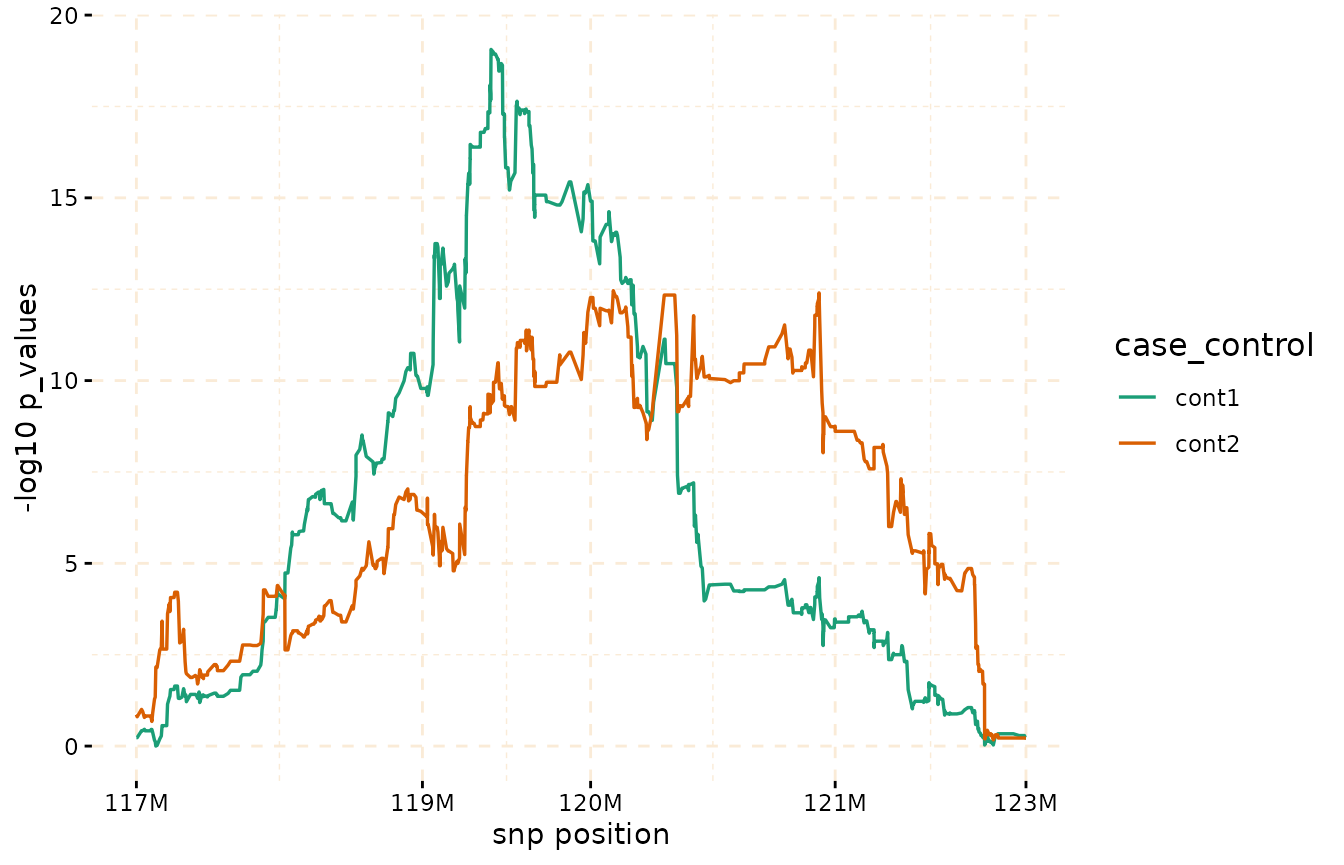
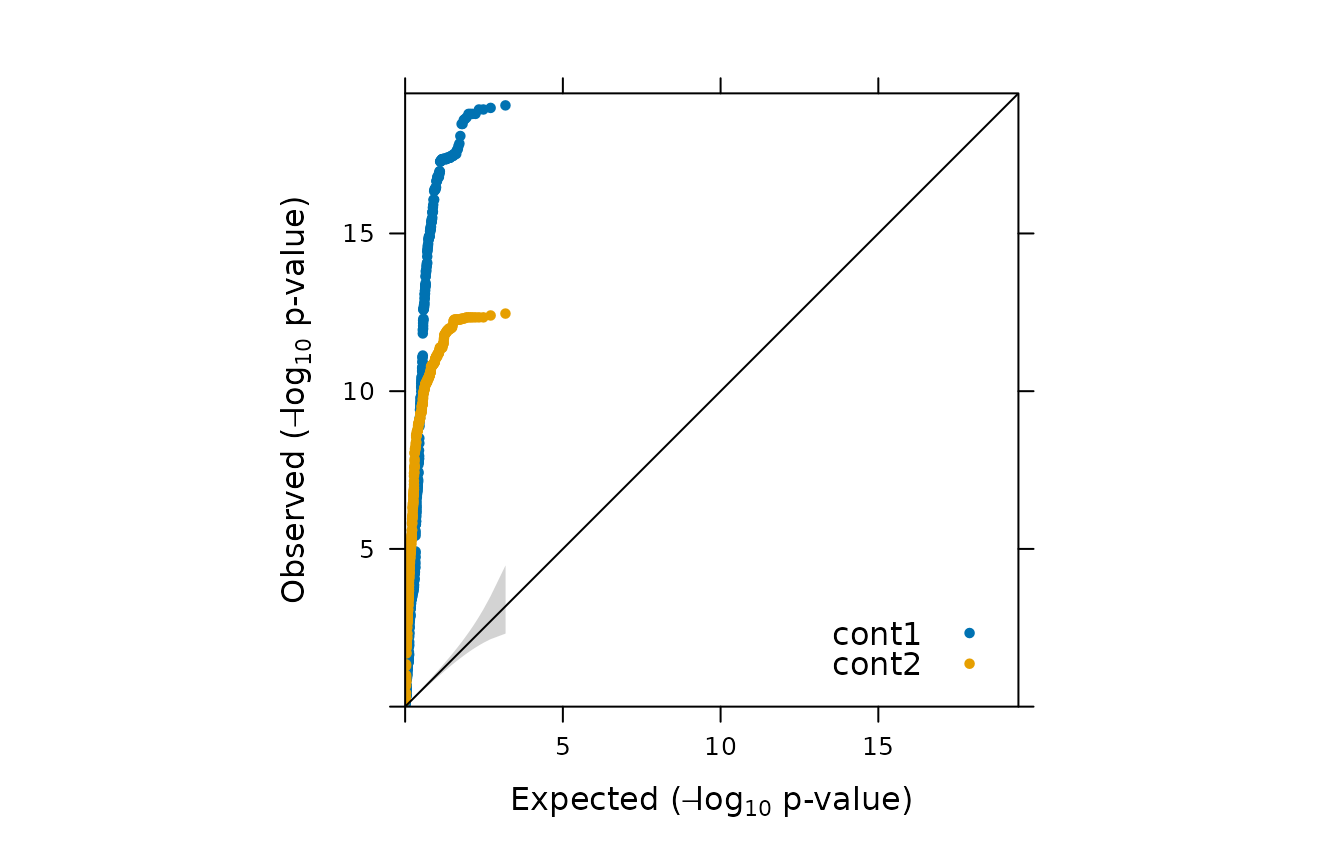
You can perform permutation test as follows:
model_permutation <- gwid::permutation_test(ibd_data,gwas = snp_data_gds,
reference = "cases",
snp_start = 117026294,
snp_end = 122613594,
nperm = 100)
plot(model_permutation,
y = c("cont1","cont2","cont3"),
log_transformation=TRUE)The haplotype_structure method can be utilized to
extract haplotypes from regions that exhibit IBD patterns in a sliding
window manner. w is length of sliding window and
hap_str <- gwid::haplotype_structure(ibd_data,
phase = haplotype_data,
w = 10,
snp_start = 117026294,
snp_end = 122613594)
class(hap_str)
#> [1] "haplotype_structure" "data.table" "data.frame"
hap_str[sample(1:nrow(hap_str),size = 5),] # structures column
#> case_control snp_pos window_number smp structures
#> <fctr> <num> <int> <char> <char>
#> 1: cases 120181419 419 3454748-1-0238060659 0000100000
#> 2: cont3 119885931 378 MC.161274@1075690254 0000000000
#> 3: cont2 118865332 195 MC.160391@1075678815 0000000000
#> 4: cases 120536346 452 MC.AMD128793@0123860942 0100000000
#> 5: cont2 118955888 217 MC.AMD102491@0124013456 0000000010
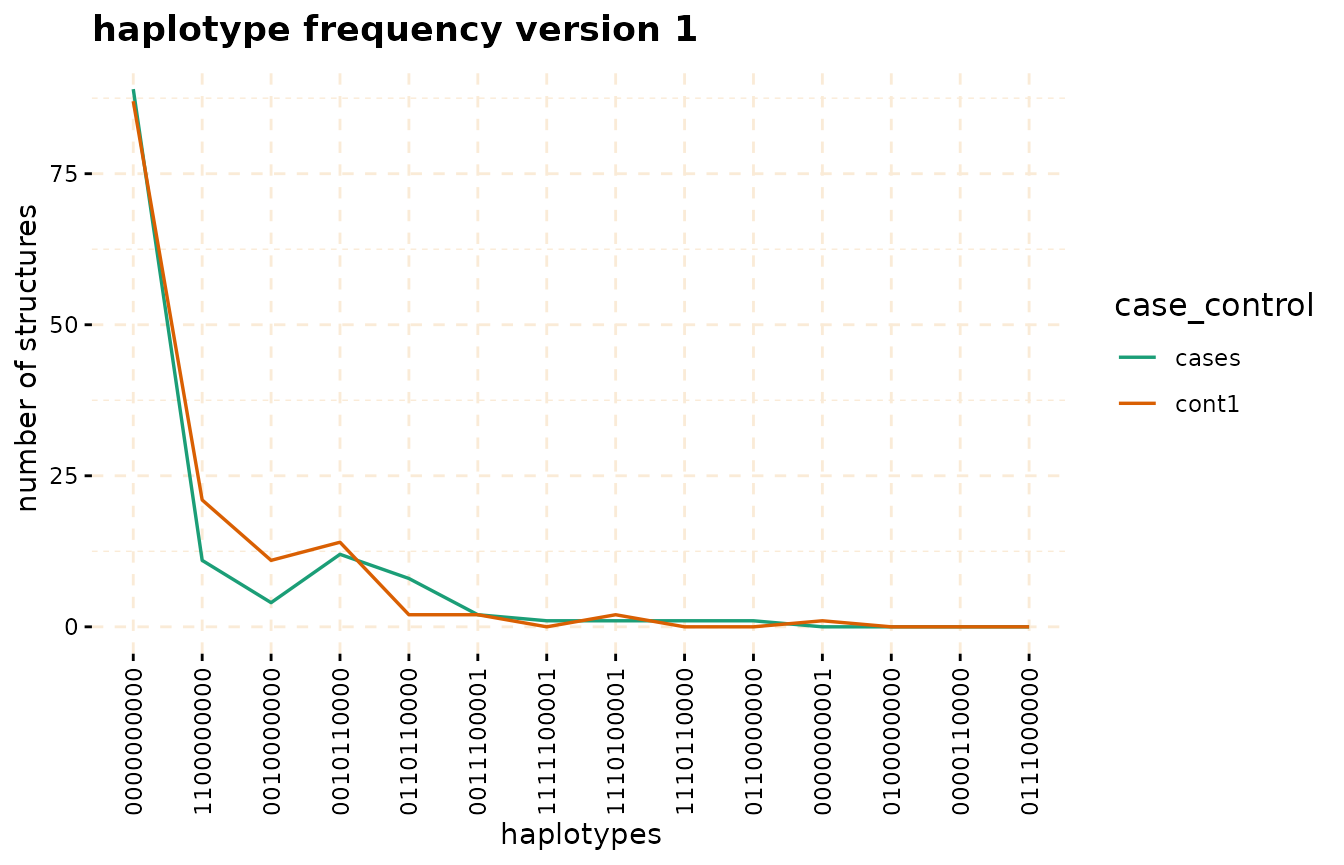
#have haplotype of length w=10 The haplotype_frequency method can be employed to
extract the count of these structures, which can then be plotted for
each window.
haplo_freq <- gwid::haplotype_frequency(hap_str)
# plot haplotype counts in first window (nwin=1).
plot(haplo_freq,
y = c("cases", "cont1"),
plot_type = "haplotype_structure_frequency",
nwin = 1, type = "version1",
ly=FALSE
)